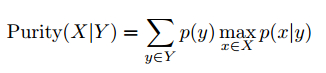
(1) code for mixture of hierarchical sparse FRAME models (2) code for mixture of And-Or templates (3) link to code for other methods
|
Contents 1: Experiment Setup 2: Clustering Dataset 3: Clustering Evaluation 4: Comparison 5: Reference |
To evaluate the clustering quality, we introduce two metrics: conditional purity and conditional entropy. Given the underlying groundtruth category labels X (which is unknown to the algorithm) and the obtained cluster labels Y , the conditional purity is defined as the mean of the maximum category probabilities for (X, Y ),
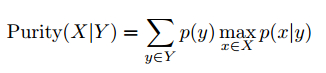
and the conditional entropy is defined as,
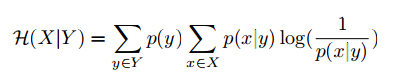
where both p(y) and p(x|y) are estimated on the training set, and we would expect higher purity and lower entropy for a better clustering algorithm.
We compare clustering by hierarchical sparse FRAME model with (1) original sparse FRAME by matching pursuit [4], (2) sparse FRAME by generative boosting [5], (3) active basis model [1], (4) two-way EM [2], (5) k-mean with HOG features, and (6) And-Or Template [3].
The methods are evaluated in terms of conditional purity and conditional entropy. All the results are obtained based on 5 repetitions. It can be seen that our method performs significantly better than other methods.
Description |
# Clusters |
Examples |
# Images |
|
Task 1 |
bull & cow |
2 |
  |
15/15 |
Task 2 |
cup & teapot |
2 |
  |
15/15 |
Task 3 |
plane & helicopter |
2 |
  |
15/15 |
Task 4 |
camel, elephant, & deer |
3 |
   |
15/15/15 |
Task 5 |
clocks (square, circle, triangle) |
3 |
   |
15/15/15 |
Task 6 |
seagull, swan, & eagle |
3 |
   |
15/15/15 |
Task 7 |
eye, nose, mouth, & ear |
4 |
    |
15/15/15/15 |
Task 8 |
flowers |
4 |
    |
15/15/15/15 |
Task 9 |
keyboard, mouse, monitor, & mainframe |
4 |
    |
15/15/15/15 |
Task 10 |
tiger, lion, cat, deer, & wolf |
5 |
     |
15/15/15/15/15 |
Task 11 |
musical intrument |
5 |
     |
15/15/15/15/15 |
Task 12 |
animal bodies |
5 |
     |
15/15/15/15/15 |
Trial |
Task 1 |
Task 2 |
Task 3 |
Task 4 |
Task 5 |
Task 6 |
Task 7 |
Task 8 |
Task 9 |
Task 10 |
Task 11 |
Task 12 |
||||||||||||
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
|
1 (seed=1) |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0.9667 |
0.1247 |
0.8667 |
0.2792 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0.9667 |
0.1236 |
0.9333 |
0.1630 |
0.9333 |
0.2124 |
1 |
0 |
0.9600 |
0.1284 |
2 (seed=2) |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0.8833 |
0.2293 |
0 |
0 |
0.9667 |
0.1026 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0.8800 |
0.2383 |
3 (seed=3) |
0.9667 |
0.1247 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0.7778 |
0.4059 |
0.9778 |
0.0831 |
1 |
0 |
0.9833 |
0.0623 |
1 |
0 |
0.9667 |
0.1026 |
0.9600 |
0.1505 |
1 |
0 |
0.9467 |
0.1304 |
4 (seed=4) |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0.9778 |
0.0831 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0.9833 |
0.0623 |
1 |
0 |
0.9333 |
0.1630 |
0.8933 |
0.2655 |
1 |
0 |
0.7867 |
0.3647 |
5 (seed=5) |
1 |
0 |
0.9667 |
0.1247 |
1 |
0 |
0.9778 |
0.0831 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0.7500 |
0.3466 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0.7467 |
0.4715 |
0.8000 |
0.2773 |
0.9733 |
0.0821 |
Trial |
Task 1 |
Task 2 |
Task 3 |
Task 4 |
Task 5 |
Task 6 |
Task 7 |
Task 8 |
Task 9 |
Task 10 |
Task 11 |
Task 12 |
||||||||||||
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
|
1 (seed=1) |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0.9556 |
0.1368 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0.9667 |
0.1026 |
0.9833 |
0.0623 |
0.9067 |
0.2449 |
1 |
0 |
0.9467 |
0.1642 |
2 (seed=2) |
1 |
0 |
0.9667 |
0.1247 |
0.9667 |
0.1247 |
0.9333 |
0.1802 |
0.9778 |
0.0831 |
1 |
0 |
0.6333 |
0.5824 |
1 |
0 |
0.7500 |
0.3578 |
0.7200
|
0.6007 |
0.7867 |
0.3579 |
0.9067 |
0.2385 |
3 (seed=3) |
0.9667 |
0.1247 |
1 |
0 |
0.8333 |
0.3749 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0.9833 |
0.0623 |
0.8333 |
0.3620 |
0.9833 |
0.0623 |
0.7200 |
0.5323 |
1 |
0 |
0.9067 |
0.2174 |
4 (seed=4) |
0.9333 |
0.2449 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0.9778 |
0.0831 |
0.9778 |
0.0831 |
1 |
0 |
0.9667 |
0.1026 |
0.9667 |
0.1257 |
0.7500 |
0.4707 |
0.8933 |
0.2716 |
0.7733 |
0.3684 |
0.9467 |
0.1606 |
5 (seed=5) |
0.9333 |
0.2449 |
0.9333 |
0.2053 |
1 |
0 |
0.6667 |
0.6078 |
0.9778 |
0.0831 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0.7467 |
0.4775 |
0.8000 |
0.2288
|
0.8267 |
0.3315 |
Trial |
Task 1 |
Task 2 |
Task 3 |
Task 4 |
Task 5 |
Task 6 |
Task 7 |
Task 8 |
Task 9 |
Task 10 |
Task 11 |
Task 12 |
||||||||||||
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
|
1 (seed=1) |
1 |
0 |
0.9667 |
0.1247 |
0.9333 |
0.2053 |
0.9778 |
0.0831 |
0.9778 |
0.0831 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0.9833 |
0.0623 |
1 |
0 |
0.9467 |
0.1606 |
1 |
0 |
0.9200 |
0.2392 |
2 (seed=2) |
0.9667 |
0.1247 |
0.9667 |
0.1247 |
1 |
0 |
0.9778 |
0.0831 |
0.9778 |
0.0831 |
1 |
0 |
0.7500 |
0.3466 |
0.9833 |
0.0623 |
1 |
0 |
0.9067 |
0.2741 |
1 |
0 |
0.8000 |
0.4081 |
3 (seed=3) |
0.5333 |
0.6909 |
0.9333 |
0.2053 |
1 |
0 |
0.6667 |
0.6371 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0.7667 |
0.3455 |
1 |
0 |
0.9733 |
0.0989 |
0.8133 |
0.2833 |
0.9467 |
0.1642 |
4 (seed=4) |
0.9667 |
0.1247 |
0.9333 |
0.2053 |
0.9333 |
0.2053 |
0.9778 |
0.0831 |
0.9778 |
0.0831 |
1 |
0 |
0.7500 |
0.3466 |
0.8833 |
0.2799 |
1 |
0 |
0.7733 |
0.4431 |
1 |
0 |
0.9600 |
0.1496 |
5 (seed=5) |
0.9667 |
0.1247 |
0.7333 |
0.5688 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0.9778 |
0.0831 |
1 |
0 |
0.7500 |
0.3466 |
0.9833 |
0.0623 |
0.7667 |
0.3347 |
0.8133 |
0.4528 |
0.8000 |
0.2773 |
0.7733 |
0.4898 |
Trial |
Task 1 |
Task 2 |
Task 3 |
Task 4 |
Task 5 |
Task 6 |
Task 7 |
Task 8 |
Task 9 |
Task 10 |
Task 11 |
Task 12 |
||||||||||||
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
|
1 (seed=1) |
0.8333 |
0.3749 |
0.9333 |
0.2053 |
0.9667 |
0.1247 |
0.9556 |
0.1648 |
0.6000 |
0.6855 |
1 |
0 |
0.9000 |
0.2384 |
0.9833 |
0.0623 |
0.9333 |
0.1630 |
0.8800 |
0.3015 |
0.7867 |
0.4195 |
0.8267 |
0.3251 |
2 (seed=2) |
0.6000 |
0.6690 |
0.9333 |
0.2053 |
1 |
0 |
0.7556 |
0.4981 |
0.7556 |
0.5486 |
0.7111 |
0.4488 |
0.6500 |
0.5410 |
0.7500 |
0.3666 |
0.7333 |
0.4966 |
0.7067 |
0.6200 |
0.9467 |
0.1555 |
0.8000 |
0.3636 |
3 (seed=3) |
0.5333 |
0.6909 |
0.7000 |
0.6104 |
0.9000 |
0.3210 |
0.5333 |
0.9132 |
0.6222 |
0.6552 |
0.7333 |
0.4122 |
0.9333 |
0.1975 |
0.9833 |
0.0623 |
0.9833 |
0.0623 |
0.8800 |
0.2656 |
1 |
0 |
0.9333 |
0.2079 |
4 (seed=4) |
0.7667 |
0.5156 |
0.6667 |
0.6354 |
0.9667 |
0.1247 |
0.7111 |
0.6793 |
0.7333 |
0.6400 |
1 |
0 |
0.7500 |
0.3722 |
0.8167 |
0.3255 |
0.9833 |
0.0623 |
0.7867 |
0.4418 |
0.9600 |
0.1081 |
0.8267 |
0.2871 |
5 (seed=5) |
0.6000 |
0.6726 |
0.7000 |
0.6104 |
0.9667 |
0.1247 |
0.6889 |
0.7152 |
0.5778 |
0.7613 |
0.7333 |
0.4367 |
0.9167 |
0.2562 |
0.9833 |
0.0623 |
0.9833 |
0.0623 |
0.7333 |
0.6069 |
0.7467 |
0.4413 |
0.6400 |
0.5848 |
Trial |
Task 1 |
Task 2 |
Task 3 |
Task 4 |
Task 5 |
Task 6 |
Task 7 |
Task 8 |
Task 9 |
Task 10 |
Task 11 |
Task 12 |
||||||||||||
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
|
1 (seed=1) |
0.9333 |
0.2053 |
0.9333 |
0.2053 |
0.5667 |
0.6842 |
0.7566 |
0.5963 |
0.9556 |
0.1648 |
1 |
0 |
0.7500 |
0.3466 |
0.8167 |
0.4644 |
1 |
0 |
0.9600 |
0.1320 |
0.8667 |
0.2987 |
0.7867 |
0.4862 |
2 (seed=2) |
0.8667 |
0.3259 |
0.9000 |
0.3210 |
0.7000 |
0.5293 |
0.7333 |
0.5910 |
0.6667 |
0.6097 |
0.9778 |
0.0831 |
0.6667 |
0.6654 |
0.7000 |
0.5957 |
0.75 |
0.3906 |
0.7467 |
0.5010 |
0.7733 |
0.4954 |
0.9200 |
0.2943 |
3 (seed=3) |
0.8333 |
0.4488 |
0.8667 |
0.3259 |
0.8000 |
0.4952 |
0.5778 |
0.7961 |
0.9556 |
0.1368 |
0.6667 |
0.5621 |
0.6667 |
0.6570 |
0.7500 |
0.5391 |
0.7667 |
0.4907 |
0.9467 |
0.1994 |
0.6933 |
0.5516 |
0.7333 |
0.6262 |
4 (seed=4) |
0.8000 |
0.5004 |
0.6000 |
0.6726 |
0.9000 |
0.3210 |
0.8889 |
0.3437 |
0.9556 |
0.1648 |
0.6889 |
0.5993 |
0.8667 |
0.2477 |
0.7167 |
0.5546 |
0.9833 |
0.0623 |
0.7733 |
0.4557 |
0.8400 |
0.4348 |
0.9200 |
0.2771 |
5 (seed=5) |
0.9333 |
0.2449 |
0.8000 |
0.4952 |
0.6000 |
0.6183 |
0.6444 |
0.6404 |
0.7556 |
0.4349 |
0.6667 |
0.5297 |
0.9167 |
0.1874 |
0.6667 |
0.6065 |
0.7500 |
0.4582 |
0.9200 |
0.2184 |
0.6133 |
0.6498 |
0.7067 |
0.6093 |
Trial |
Task 1 |
Task 2 |
Task 3 |
Task 4 |
Task 5 |
Task 6 |
Task 7 |
Task 8 |
Task 9 |
Task 10 |
Task 11 |
Task 12 |
||||||||||||
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
|
1 (seed=1) |
0.9333 |
0.2053 |
0.6000 |
0.6714 |
0.9333 |
0.2449 |
0.8222 |
0.5066 |
0.9333 |
0.2200 |
1 |
0 |
0.7833 |
0.3233 |
0.8667 |
0.3665 |
0.7500 |
0.3826 |
0.5600 |
0.7235 |
0.8667 |
0.2616 |
0.8800 |
0.2802 |
2 (seed=2) |
0.8667 |
0.3927 |
0.8000 |
0.4952 |
0.9000 |
0.3210 |
0.8667 |
0.3806 |
0.6444 |
0.5862 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0.8333 |
0.4485 |
0.9667 |
0.1247 |
0.5600 |
0.7562 |
0.6933 |
0.5580 |
0.6933 |
0.5877 |
3 (seed=3) |
0.5000 |
0.6931 |
0.6333 |
0.6556 |
0.8333 |
0.4326 |
0.8889 |
0.3435 |
0.7556 |
0.4570 |
1 |
0 |
0.7500 |
0.3466 |
0.7500 |
0.5345 |
0.9833 |
0.0623 |
0.8133 |
0.2756 |
0.7867 |
0.4315 |
0.7067 |
0.6232 |
4 (seed=4) |
0.7000 |
0.6068 |
0.5667 |
0.6839 |
0.8000 |
0.4767 |
0.6889 |
0.6098 |
0.9333 |
0.2200 |
0.6667 |
0.4621 |
0.7500 |
0.3466 |
0.7500 |
0.5989 |
0.7500 |
0.3971 |
0.8800 |
0.3590 |
0.7867 |
0.3281 |
0.7867 |
0.4229 |
5 (seed=5) |
0.8000 |
0.4952 |
0.6000 |
0.6714 |
0.5000 |
0.6931 |
0.7333 |
0.6164 |
0.9333 |
0.1802 |
1 |
0 |
0.7500 |
0.3466 |
0.7000 |
0.6461 |
0.7500 |
0.3578 |
0.7600 |
0.4632 |
0.7867 |
0.3537 |
0.7733 |
0.4721 |
Trial |
Task 1 |
Task 2 |
Task 3 |
Task 4 |
Task 5 |
Task 6 |
Task 7 |
Task 8 |
Task 9 |
Task 10 |
Task 11 |
Task 12 |
||||||||||||
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
purity |
entropy |
|
1 (seed=1) |
0.9 |
0.2703 |
0.8667 |
0.3259 |
0.9333 |
0.2449 |
0.6222 |
0.7788 |
0.9556 |
0.1368 |
1 |
0 |
0.7500 |
0.3466 |
1 |
0 |
0.7000 |
0.5441 |
0.7867 |
0.4269 |
1 |
0 |
0.8000 |
0.4111 |
2 (seed=2) |
0.9333 |
0.2053 |
0.9667 |
0.1247 |
1 |
0 |
0.9556 |
0.1368 |
0.7778 |
0.4851 |
1 |
0 |
0.7500 |
0.4738 |
0.7333 |
0.3916 |
0.9833 |
0.0623 |
0.9867 |
0.0499 |
1 |
0 |
0.6267 |
0.6235 |
3 (seed=3) |
0.5333 |
0.6909 |
0.8667 |
0.3259 |
1 |
0 |
0.9111 |
0.2634 |
0.8222 |
0.4302 |
1 |
0 |
0.9333 |
0.2226 |
0.6167 |
0.5942 |
1 |
0 |
0.7733 |
0.4897 |
0.9867 |
0.0499 |
0.8267 |
0.3160 |
4 (seed=4) |
0.9000 |
0.2703 |
0.6000 |
0.6645 |
0.9667 |
0.1247 |
0.9333 |
0.1802 |
0.9333 |
0.2227 |
1 |
0 |
0.7500 |
0.4216 |
0.7500 |
0.3666 |
0.9667 |
0.1247 |
0.7867 |
0.4743 |
1 |
0 |
0.5467 |
0.8939 |
5 (seed=5) |
0.8000 |
0.4188 |
0.5667 |
0.6817 |
0.6333 |
0.5904 |
0.9556 |
0.1648 |
0.7556 |
0.5479 |
1 |
0 |
0.9667 |
0.1026 |
0.7500 |
0.3784 |
0.7500 |
0.3466 |
0.7867 |
0.3537 |
0.8133 |
0.2678 |
0.7600 |
0.4701 |
Exp1 |
Exp2 |
Exp3 |
Exp4 |
Exp5 |
Exp6 |
Exp7 |
Exp8 |
Exp9 |
Exp10 |
Exp11 |
Exp12 |
|
k-means with HOG |
0.7600 ± 0.1690 |
0.6400 ± 0.0925 |
0.7933 ± 0.1722 |
0.8000 ± 0.0861 |
0.8400 ± 0.1337 |
0.9333 ± 0.1491 |
0.8067 ± 0.1090 |
0.7800 ± 0.0681 |
0.8400 ± 0.1234 |
0.7147 ± 0.1474 |
0.7840 ± 0.0614 |
0.7680 ± 0.0746 |
two way EM |
0.8733 ± 0.0596 |
0.8200 ± 0.1325 |
0.7133 ± 0.1386 |
0.7202 ± 0.1183 |
0.8578 ± 0.1375 |
0.8000 ± 0.1728 |
0.7734 ± 0.1146 |
0.7300 ± 0.0570 |
0.8500 ± 0.1296 |
0.8693 ± 0.1013 |
0.7573 ± 0.1048 |
0.8133 ± 0.1015 |
Active Basis model |
0.6667 ± 0.1269 |
0.7867 ± 0.1346 |
0.9600 ± 0.0365 |
0.7289 ± 0.1519 |
0.6578 ± 0.0810 |
0.8355 ± 0.1504 |
0.8300 ± 0.1244 |
0.9033 ± 0.1120 |
0.9233 ± 0.1084 |
0.7973 ± 0.0808 |
0.8880 ± 0.1134 |
0.8053 ± 0.1057 |
sparse FRAME (by generative boosting) |
0.8867 ± 0.1981 |
0.9067 ± 0.0983 |
0.9733 ± 0.0365 |
0.9200 ± 0.1419 |
0.9822 ± 0.0099 |
1.0000 ± 0.0000 |
0.8500 ± 0.1369 |
0.9200 ± 0.0960 |
0.9533 ± 0.1043 |
0.8827 ± 0.0861 |
0.9227 ± 0.1060 |
0.8800 ± 0.0869 |
sparse FRAME (by matching pursuit) |
0.9667 ± 0.0334 |
0.9800 ± 0.0298 |
0.9600 ± 0.0723 |
0.9067 ± 0.1364 |
0.9867 ± 0.0122 |
1.0000 ± 0.0000 |
0.9167 ± 0.1590 |
0.9533 ± 0.0691 |
0.8933 ± 0.1310 |
0.7973 ± 0.0945 |
0.8720 ± 0.1172 |
0.9067 ± 0.0490 |
And-Or Template (AOT) |
0.8133 ± 0.1643 |
0.7734 ± 0.1786 |
0.9067 ± 0.1553 |
0.8756 ± 0.1428 |
0.8489 ± 0.0908 |
1.0000 ± 0.0000 |
0.8300 ± 0.1102 |
0.7700 ± 0.1401 |
0.8800 ± 0.1431 |
0.8240 ± 0.0911 |
0.9600 ± 0.0822 |
0.7120 ± 0.1202 |
hierarchical sparse FRAME |
0.9933 ± 0.0149 |
0.9933 ± 0.0149 |
0.9933 ± 0.0149 |
0.9200 ± 0.0951 |
0.9956 ± 0.0099 |
1.0000 ± 0.0000 |
0.9200 ± 0.1057 |
0.9933 ± 0.0149 |
0.9600 ± 0.0250 |
0.9067 ± 0.0975 |
0.9600 ± 0.0894 |
0.9093 ± 0.0774 |
Exp1 |
Exp2 |
Exp3 |
Exp4 |
Exp5 |
Exp6 |
Exp7 |
Exp8 |
Exp9 |
Exp10 |
Exp11 |
Exp12 |
|
k-means with HOG |
0.4786 ± 0.1903 |
0.6355 ± 0.0791 |
0.4337 ± 0.1714 |
0.4914 ± 0.1265 |
0.3327 ± 0.1791 |
0.0924 ± 0.2067 |
0.2724 ± 0.1527 |
0.5189 ± 0.1129 |
0.2649 ± 0.1586 |
0.5155 ± 0.2156 |
0.3866 ± 0.1135 |
0.4772 ± 0.1372 |
two way EM |
0.3451 ± 0.1273 |
0.4040 ± 0.1823 |
0.5296 ± 0.1383 |
0.5935 ± 0.1625 |
0.3022 ± 0.2105 |
0.3548 ± 0.2886 |
0.4208 ± 0.2267 |
0.5521 ± 0.0564 |
0.2804 ± 0.2314 |
0.3013 ± 0.1656 |
0.4861 ± 0.1313 |
0.4586 ± 0.1670 |
Active Basis model |
0.5846 ± 0.1368 |
0.4534 ± 0.2267 |
0.1390 ± 0.1152 |
0.5941 ± 0.2816 |
0.6581 ± 0.0770 |
0.2595 ± 0.2373 |
0.3211 ± 0.1390 |
0.1758 ± 0.1561 |
0.1693 ± 0.1881 |
0.4472 ± 0.1655 |
0.2249 ± 0.1960 |
0.3537 ± 0.1414 |
sparse FRAME (by generative boosting) |
0.2130 ± 0.2726 |
0.2457 ± 0.1850 |
0.0821 ± 0.1124 |
0.1773 ± 0.2596 |
0.0665 ± 0.0372 |
0.0000 ± 0.0000 |
0.2080 ± 0.1898 |
0.1625 ± 0.1391 |
0.0669 ± 0.1497 |
0.2859 ± 0.1608 |
0.1121 ± 0.1535 |
0.2902 ± 0.1517 |
sparse FRAME (by matching pursuit) |
0.1229 ± 0.1225 |
0.0660 ± 0.0948 |
0.0999 ± 0.1629 |
0.2016 ± 0.2368 |
0.0499 ± 0.0455 |
0.0000 ± 0.0000 |
0.1495 ± 0.2459 |
0.1181 ± 0.1481 |
0.1906 ± 0.2096 |
0.4254 ±0.1590 |
0.1910 ± 0.1828 |
0.2224 ± 0.0696 |
And-Or Template (AOT) |
0.3711 ± 0.1952 |
0.4245 ± 0.2414 |
0.1920 ± 0.2448 |
0.3048 ± 0.2691 |
0.3645 ± 0.1764 |
0.0000 ± 0.0000 |
0.3134 ± 0.1510 |
0.3462 ± 0.2150 |
0.2155 ± 0.2255 |
0.3589 ± 0.1807 |
0.0635 ± 0.1162 |
0.5429 ± 0.2258 |
hierarchical sparse FRAME |
0.0249 ± 0.0558 |
0.0249 ± 0.0558 |
0.0249 ± 0.0558 |
0.1703 ± 0.1670 |
0.0166 ± 0.0372 |
0.0000 ± 0.0000 |
0.1401 ± 0.1435 |
0.0247 ± 0.0553 |
0.1062 ± 0.0666 |
0.2200 ± 0.1722 |
0.0555 ± 0.1240 |
0.1888 ± 0.1138 |